Linux基本重要操作指令:
cd變換目錄, pwd(PrintWorkingDirectory)顯示當下路徑,
mkdir/rmdir(MakeDirectory/RemoveDirectory)建立/刪除目錄, ls顯示檔案名稱, cp(copy)複製貼上,
rm(remove)刪除檔案, rm -rf (re force)強制刪除資料夾, mv (move) 移動,
less觀看檔案內容, vi文書處理 --> i編輯 --> esc一般模式 --> :wq儲存離開, :q!離開不儲存
座標建立:
1. 直角座標
2. 分子內部座標


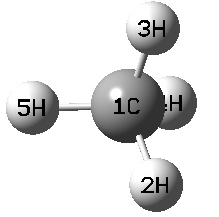
ex: CH4
1 C
2 H 1 R
3 H 1 R 2 A
4 H 1 R 2 A 3 D
5 H 1 R 2 A 3 -D
R=1.07
A=109.47122
D=120
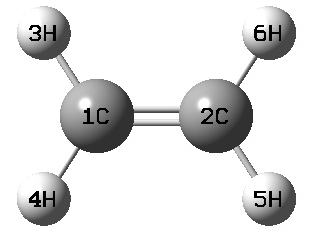
ex: C2H4
1 C
2 C 1 R1
3 H 1 R2 2 A1
4 H 1 R2 2 A1 3 180
5 H 2 R2 1 A1 3 180
6 H 2 R2 1 A1 3 0
Single Point Energy Calculation:
ex: #T RHF/6-31G(d) Pop=Full Test
#T: request terse output from program
method HF: 使用 Hartree-Fock 理論,也就是用一個行列式 (slater determinant) 來代表波函數
(mp2, mp3 ...)
R: restricted (U: unrestricted)
basis 6-31G(d):
這K個AO就稱為計算使用之基底函數
(basis functions or basis set)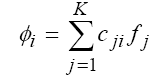
job Pop=Full
最後求得能量、分子軌域、軌域能量、Charges、Dipole 和 Multipole moments…等
ex: Propene Single Point (#T RHF/6-31G(d) Test)
Hartree-Fock energy: SCF Done: E(RHF) = -117.065692097 A.U. after 5 cycles
Mulliken atomic
charges:
1
1 C -0.388759
2 C -0.156384
3 C -0.507949
4 H 0.170153
5 H 0.173467
6 H 0.184153
7 H 0.165601
8 H 0.179859
9 H 0.179859
Sum of Mulliken charges= 0.00000
Dipole moment (field-independent basis, Debye):
X= -0.3030 Y= -0.0298 Z= 0.0000 Tot= 0.3045
Geometry Optimization:
Optimization的目的是為了找出PES的min => Convergence Criteria => 求得最佳化結構
ex: #T RHF/6-31G(d) Opt Test
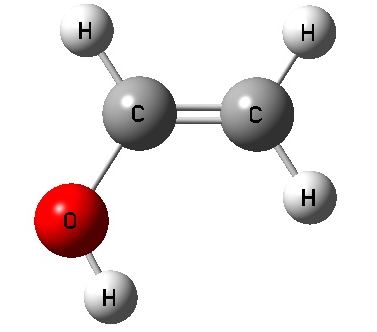
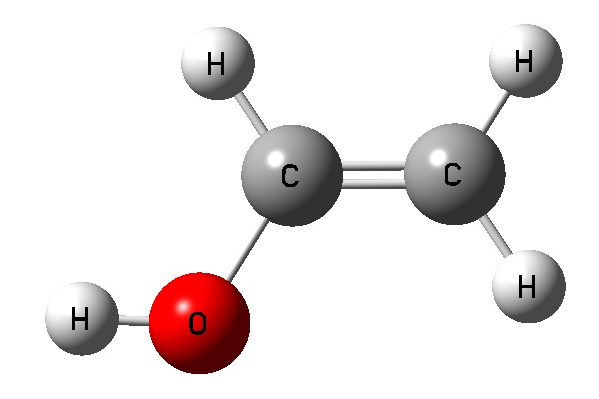
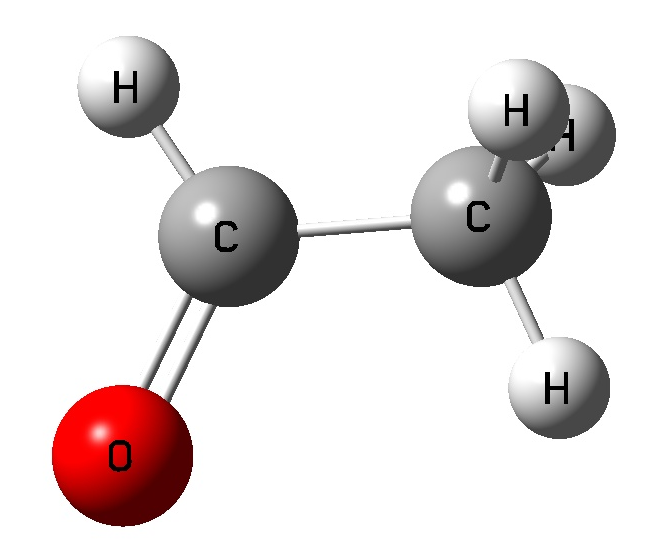
Vinyl Alcohol CCOH=0 Vinyl Alcohol CCOH=180 Acetaldehyde
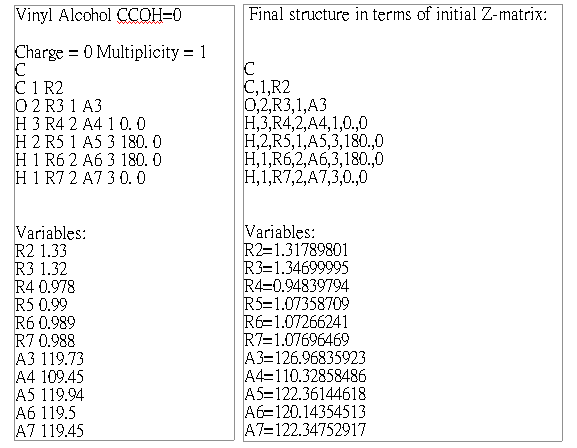
Vinyl Alcohol CCOH=0 Geom.
Opt.
SCF Done: E(RHF) = -152.888886562 A.U. after 8 cycles
Vinyl Alcohol CCOH=180 Geom. Opt.
SCF Done: E(RHF) = -152.885388871 A.U. after 10 cycles
Acetaldehyde Geom. Opt.
SCF Done: E(RHF) = -152.915965413 A.U. after 8 cycles
變換 basis set 及不同方法求相同的分子, 看其與實驗數據的差別, 還有計算上的效率
(MNDO, PM3, HF/STO-3G, HF/3-21G)
Reactant => Product 之間的 Transition Structure 最佳化